What is Lean Six Sigma?
The combination of two globally proven methodologies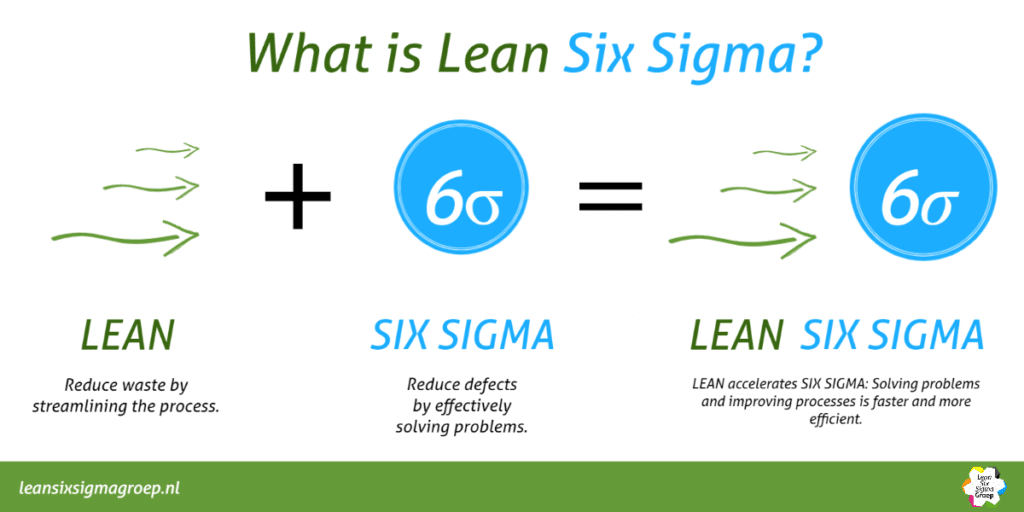
Lean Six Sigma is a globally proven methodology for the sustainable and demonstrable improvement of processes and organizations. It offers an approach with which organizations can achieve concrete results in a structured manner (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control or DMAIC) with continuous improvement.
The starting point is focus on what customers really consider important and to realize this in processes. No more and no less. With this approach, costs are reduced, customer satisfaction is increased and the lead time is shortened. The strength of this approach is that it uses existing knowledge and experience of people within the processes.
The Lean Six Sigma method improves both the process and the quality. Lean strives for more flow and generating value. Six Sigma strives for stable and effective processes. In combination they reinforce each other and are completely complementary.
|
Table of contents
|
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF USING LEAN SIX SIGMA?
Organizations are confronted daily with rising costs and increasing competition. With Lean Six Sigma you can combat these problems and grow your business:
- Increase profit
- Reduce costs
- Improve efficiency and effectiveness
- Help employees develop
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT ROLES IN LEAN SIX SIGMA?
Process improvement is a challenge. If the right people with the right Lean Six Sigma skills are involved, significant and lasting change can be achieved. The use of the term ‘belts’, bands in Dutch, comes from Karate. This indicates the different skill levels. Here are the main roles in Lean Six Sigma:
- Yellow Belt; Understands the basics of Lean Six Sigma. Passes process problems to Green & Black Belts. Participates in project teams and receives JIT (just-in-time) training.
- Orange Belt; Can apply the basic principles of Lean Six Sigma in a practical way. Ability to lead small improvement projects.
- Green Belt; Start and manage Lean Six Sigma projects. Has Lean Six Sigma expertise but in less detail than Black Belts. Provides JIT (just-in-time) training to others.
- Black Belt; Reports directly to a Master Black Belt. Has advanced expertise in Lean Six Sigma. Acts as a coach, mentor, teacher and project leader for project teams.
- Master Black Belt; Works with leaders to identify gaps and select (improvement) projects. Provides coaching, mentorship, acts as a teacher and independently leads projects. Responsible for Lean Six Sigma implementation and culture change in a company.
Lean Six Sigma was developed from two methodologies: Lean and Six Sigma.
WHAT IS LEAN?
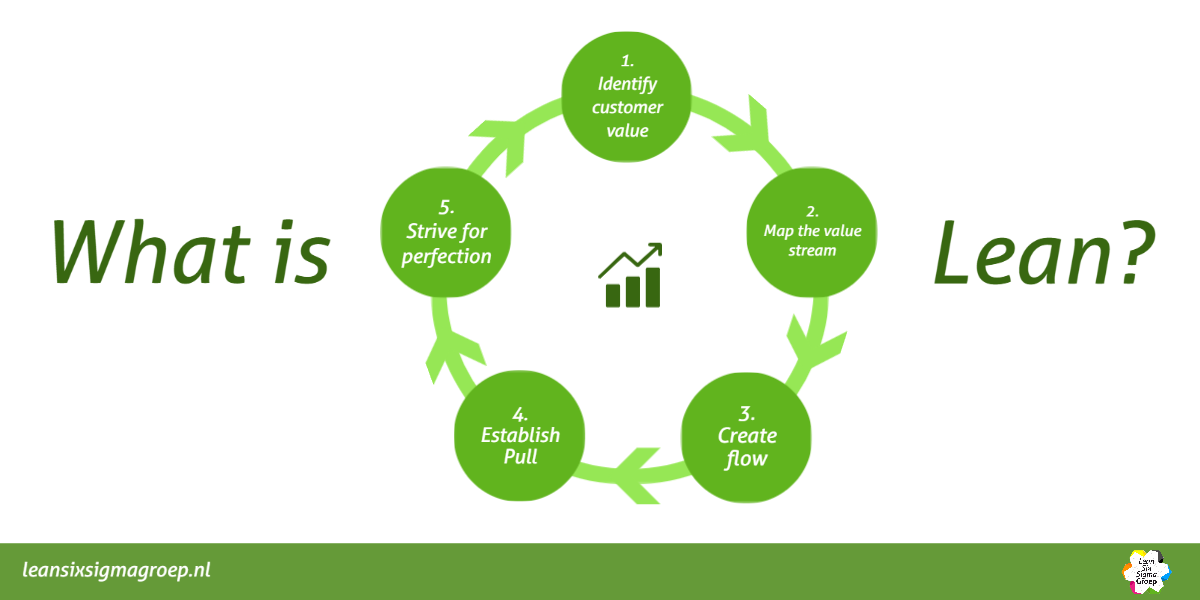
Lean’s fundamentals can be traced back to Toyota Production Systems (TPS). The Japanese Taiichi Ohno is the founder and based on developments from innovations by, for example, Henry Ford and methodologies such as Business Process Redesign.
- Lean starts with determining the added value for the customer; a product or service that meets certain conditions.
- The process that produces this value, the so-called value stream, is then mapped out.
- By carrying out this exercise, it becomes clear where wastes are and an improved process with “flow” can be made. These wastes become transparent through the collection of data around this and together with the people in the process the process improves step by step.
- Then you look at how you can set up the process so that it starts when the customer asks for it and then delivers exactly on time, when the customer wants it.
- People in the organization will see where improvements can be made and work on their own improvements. This creates an organization in which process-wide thinking and everything is focused on doing what the customer asks in a smart, effective and efficient manner.
►Read more in “What is Lean?”
WHAT IS SIX SIGMA?

Six Sigma was developed in the same time as Lean and is more data-driven. The method was developed by Motorola and widely and very successfully applied by General Electric.
The structured project approach Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control (DMAIC) ensures that the root cause of a problem is first found before a solution is implemented. By applying the DMAIC Model you use the capacities of your employees within the organizational structure in an efficient and intelligent way to create as much value for the customer as possible. A variant of this model is the DMADV or DFSS (Design For Six Sigma): Define, Measure, Analyze, Design and Verify. By determining and measuring the company’s important indicators, it becomes clear where improvements need to be made. Management receives targets and tools for this through Six Sigma and this creates a structured improvement model. As with Lean, this is based on the added value for the customer.
►Read more in What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma and Lean
The two methods are very complementary because they both start from the wishes of the customer, the process and improve it together with employees. Lean Six Sigma tackles business problems at the core and ensures continuous improvement.