The combination of two globally proven methodologies
Lean’s fundamentals can be traced back to Toyota Production Systems (TPS). The Japanese Taiichi Ohno is the founder and based on developments from innovations by, for example, Henry Ford and methodologies such as Business Process Redesign.
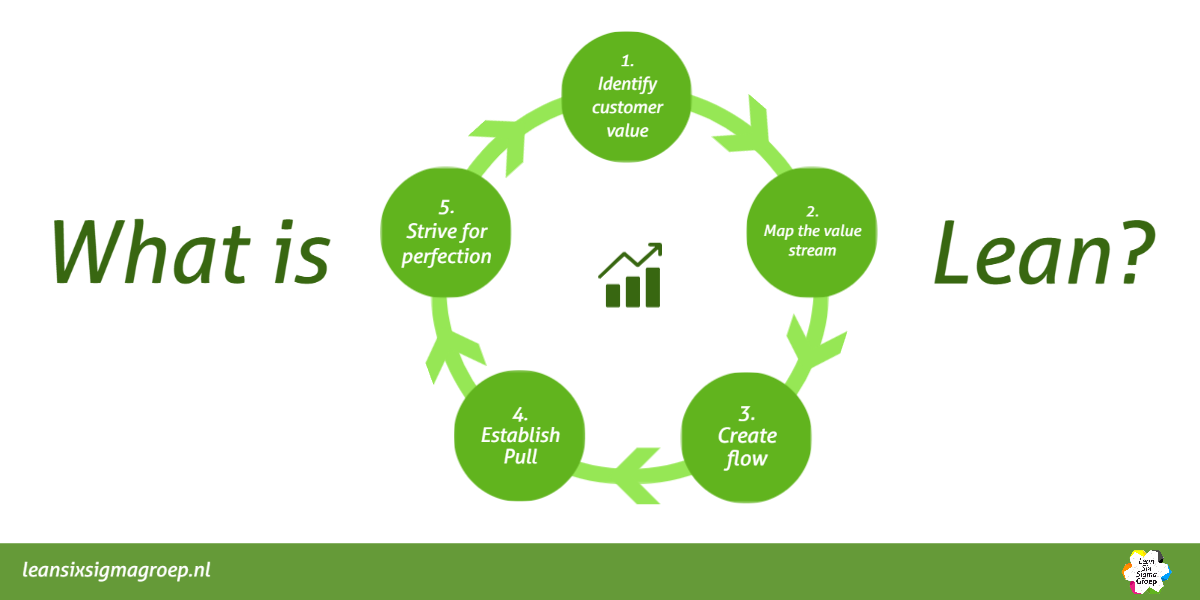
►Read more in “What is Lean?”
Six Sigma was developed in the same time as Lean and is more data-driven. The method was developed by Motorola and widely and very successfully applied by General Electric.
The structured project approach Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control (DMAIC) ensures that the root cause of a problem is first found before a solution is implemented. By applying the DMAIC Model you use the capacities of your employees within the organizational structure in an efficient and intelligent way to create as much value for the customer as possible. A variant of this model is the DMADV or DFSS (Design For Six Sigma): Define, Measure, Analyze, Design and Verify. By determining and measuring the company’s important indicators, it becomes clear where improvements need to be made. Management receives targets and tools for this through Six Sigma and this creates a structured improvement model. As with Lean, this is based on the added value for the customer.
►Read more in What is Six Sigma?
The two methods are very complementary because they both start from the wishes of the customer, the process and improve it together with employees. Lean Six Sigma tackles business problems at the core and ensures continuous improvement.
Invalid form shortcode: [activecampaign form=87 css=1]

441+ beoordelingen